Features of Business and Accounting
Introduction
Business and accounting are two fundamental pillars that support the economic activities of individuals, organizations, and entire economies. Understanding the key features of business and accounting helps entrepreneurs, financial professionals, and business owners make informed decisions and maintain financial stability. This blog explores the essential features of business and accounting, highlighting their importance, principles, and the role they play in organizational success.
Features of Business

1. Economic Activity
Business is primarily an economic activity that involves the production, distribution, and exchange of goods and services. It aims to generate profits by meeting the demands of consumers in a competitive market.
2. Profit Motive
One of the primary objectives of any business is to earn profits. While some businesses may also have social and ethical goals, profitability ensures the sustainability and growth of the organization.
3. Risk and Uncertainty
Every business operates in a dynamic environment that involves risks and uncertainties. Factors such as market competition, economic fluctuations, political changes, and technological advancements can impact business performance.
4. Production or Procurement of Goods and Services
A business either manufactures products or procures them from suppliers to sell to consumers. Similarly, service-based businesses offer professional assistance, consultancy, or digital services.
5. Exchange of Goods and Services
Business transactions involve the exchange of goods and services for money or barter. This exchange drives economic activity and facilitates the movement of resources within the economy.
6. Customer Orientation
Businesses exist to serve customers. Understanding consumer needs, preferences, and behaviors helps businesses tailor their products and services to meet market demands effectively.
7. Innovation and Adaptability
Successful businesses continuously innovate and adapt to changing market trends, technology advancements, and customer preferences. Innovation can occur in products, services, business models, or operational processes.
8. Legal Compliance
Businesses must comply with legal and regulatory frameworks. These include business registration, taxation, labor laws, environmental regulations, and industry-specific guidelines.
9. Resource Management
Effective utilization of financial, human, and material resources is crucial for business success. Strategic planning and resource allocation help businesses optimize operations and improve productivity.
10. Scalability and Growth
Businesses aim to expand their operations, reach new markets, and increase revenues over time. Scalability is an essential feature that allows businesses to sustain growth and compete effectively in the marketplace.
Features of Accounting
1. Systematic Recording of Transactions
Accounting involves the systematic recording of financial transactions in books of accounts. This ensures accuracy, consistency, and reliability in financial reporting.
2. Classification and Summarization
Transactions are classified into different categories (assets, liabilities, income, expenses) and summarized to generate financial statements such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements.
3. Financial Reporting
Accounting provides stakeholders with financial reports that help assess the financial health of a business. Investors, creditors, and management use these reports for decision-making.
4. Compliance with Accounting Standards

Accounting follows standardized principles such as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) to ensure uniformity and comparability of financial statements.
5. Double-Entry System
The double-entry system is the foundation of modern accounting, where every transaction affects two accounts. This ensures accuracy and helps in detecting errors.
6. Cost and Management Accounting
Accounting is not just about financial reporting; it also includes cost accounting (analyzing costs associated with production) and management accounting (providing internal reports for strategic decision-making).
7. Taxation and Regulatory Compliance
Accounting ensures businesses comply with tax regulations by preparing tax returns, calculating liabilities, and maintaining necessary financial records for audits.
8. Decision-Making Tool
Financial data from accounting helps businesses make informed decisions regarding investments, pricing strategies, budgeting, and expansion plans.
9. Fraud Detection and Prevention
Accounting helps in identifying discrepancies and potential fraud through internal controls, audits, and reconciliation of accounts.
10. Automation and Digitalization
Modern accounting relies on software and automation tools such as QuickBooks, Xero, and cloud-based platforms, which enhance accuracy and efficiency in financial management.
Importance of Business and Accounting
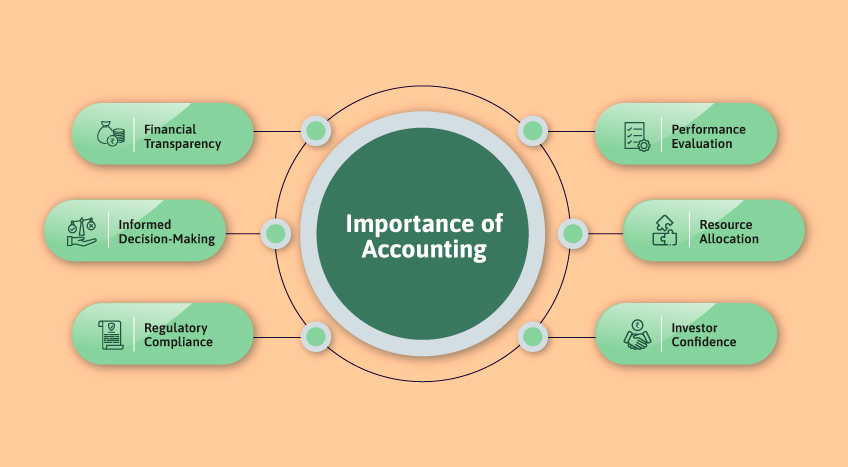
Both business and accounting play critical roles in economic development and financial stability. Here are some key reasons why they are essential:
- Financial Transparency: Accurate accounting practices ensure businesses maintain transparency and accountability.
- Investment Attraction: Investors and creditors rely on accounting reports to assess the viability of businesses before making financial commitments.
- Operational Efficiency: Sound business strategies and accounting help optimize costs and improve efficiency.
- Regulatory Compliance: Proper accounting ensures businesses meet legal requirements, avoiding penalties and legal consequences.
- Sustainable Growth: Effective business management and accounting practices support long-term sustainability and expansion.
Conclusion
Understanding the features of business and accounting is crucial for entrepreneurs, financial professionals, and investors. Business involves economic activities, customer engagement, innovation, and risk management, while accounting ensures financial accuracy, regulatory compliance, and informed decision-making. Together, they form the backbone of economic success, helping organizations achieve their goals and contribute to economic development.



